Collaborative Metric Learning (CML) recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for recommendation based on implicit feedback collaborative filtering. However, standard CML methods learn fixed user and item representations, which fails to capture the complex interests of users. Existing extensions of CML also either ignore the heterogeneity of user-item relations, i.e. that a user can simultaneously like very different items, or the latent item-item relations, i.e. that a user’s preference for an item depends, not only on its intrinsic characteristics, but also on items they previously interacted with.
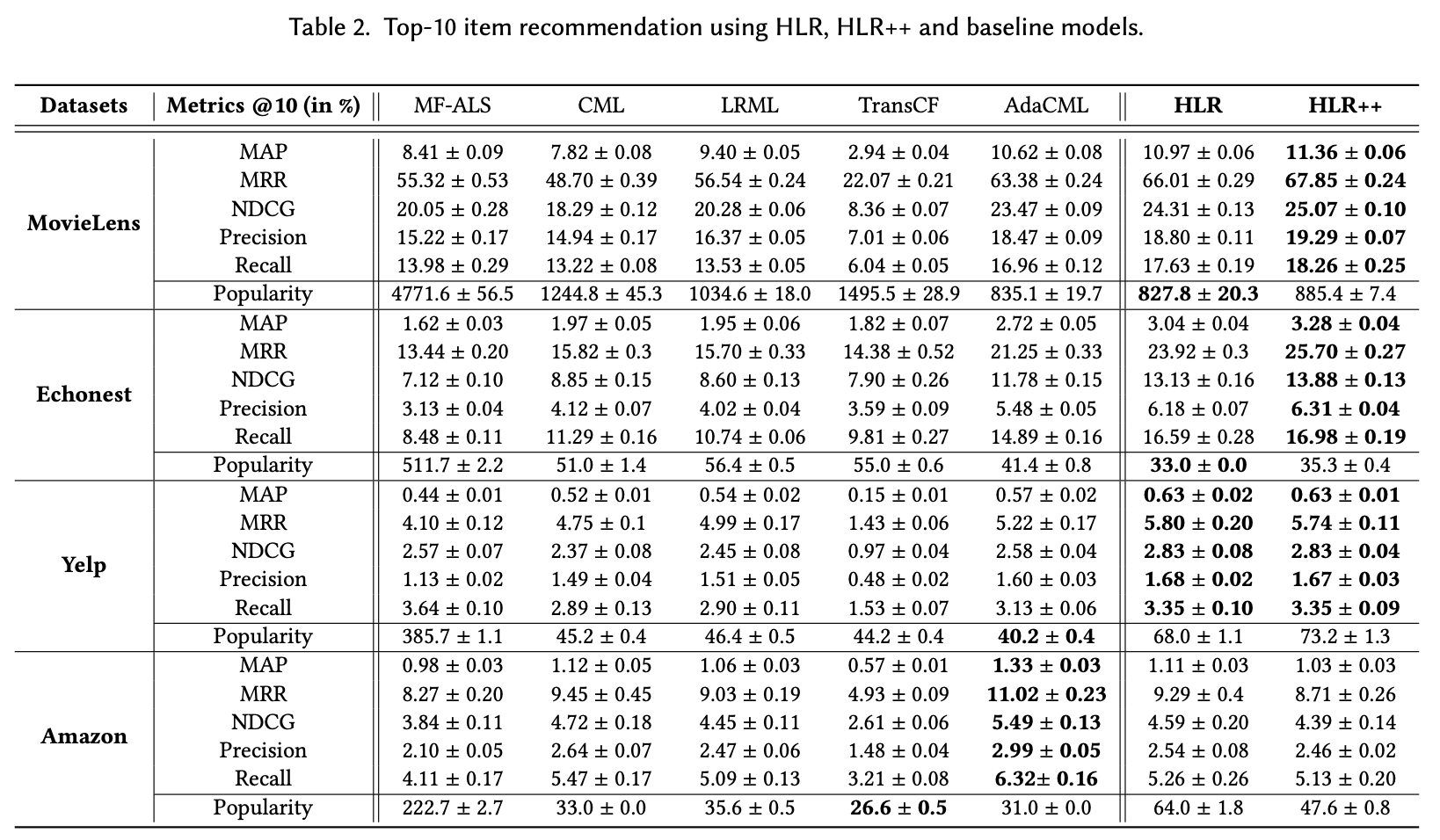
In this paper, we present a hierarchical CML model that jointly captures latent user-item and item-item relations from implicit data Our approach is inspired by translation mechanisms from knowledge graph embedding and leverages memory-based attention networks. We empirically show the relevance of this joint relational modeling, by outperforming existing CML models on recommendation tasks on several real-world datasets. Our experiments also emphasize the limits of current CML relational models on very sparse datasets.
This paper has been accepted for publication in the proceedings of the 15th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems (RecSys 2021).



