Explaining recommendations enables users to understand whether recommended items are relevant to their needs and has been shown to increase their trust in the system. More generally, if designing explainable machine learning models is key to check the sanity and robustness of a decision process and improve their efficiency, it however remains a challenge for complex architectures, especially deep neural networks that are often deemed “black-box”.
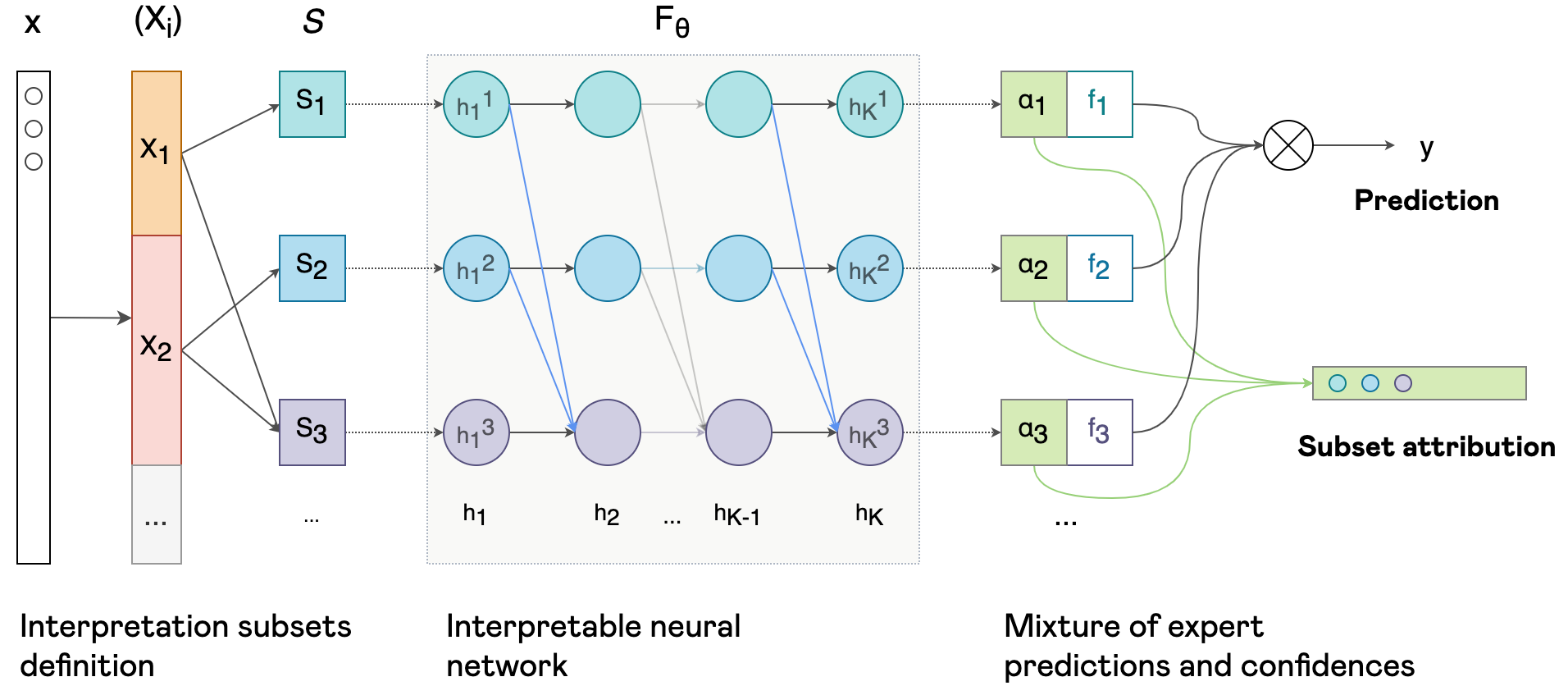
In this paper, we propose a novel formulation of interpretable deep neural networks for the attribution task. Differently to popular post-hoc methods, our approach is interpretable by design. Using masked weights, hidden features can be deeply attributed, split into several input-restricted sub-networks and trained as a boosted mixture of experts.
Experimental results on synthetic data and real-world recommendation tasks demonstrate that our method enables to build models achieving close predictive performances to their non-interpretable counterparts, while providing informative attribution interpretations.
This paper has been published in the proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems (RecSys 2020).

