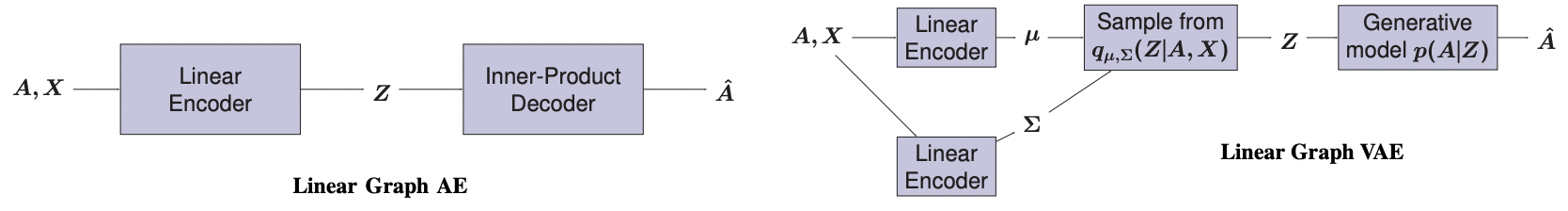
Graph autoencoders (AE) and variational autoencoders (VAE) recently emerged as powerful node embedding methods, with promising performances on challenging tasks such as link prediction and node clustering. Graph AE, VAE and most of their extensions rely on graph convolutional networks (GCN) encoders to learn vector space representations of nodes. In this paper, we propose to replace the GCN encoder by a significantly simpler linear model w.r.t. the direct neighborhood (one-hop) adjacency matrix of the graph.
For the two aforementioned tasks, we show that this approach consistently reaches competitive performances w.r.t. GCN-based models for numerous real-world graphs, including all benchmark datasets commonly used to evaluate graph AE and VAE. We question the relevance of repeatedly using these datasets to compare complex graph AE and VAE. We also emphasize the effectiveness of the proposed encoding scheme, that appears as a simpler and faster alternative to GCN encoders for many real-world applications.
This paper has been presented at the NeurIPS 2019 Workshop on Graph Representation Learning. An extended conference version of this article is also available here: Simple and Effective Graph Autoencoders with One-Hop Linear Models.

